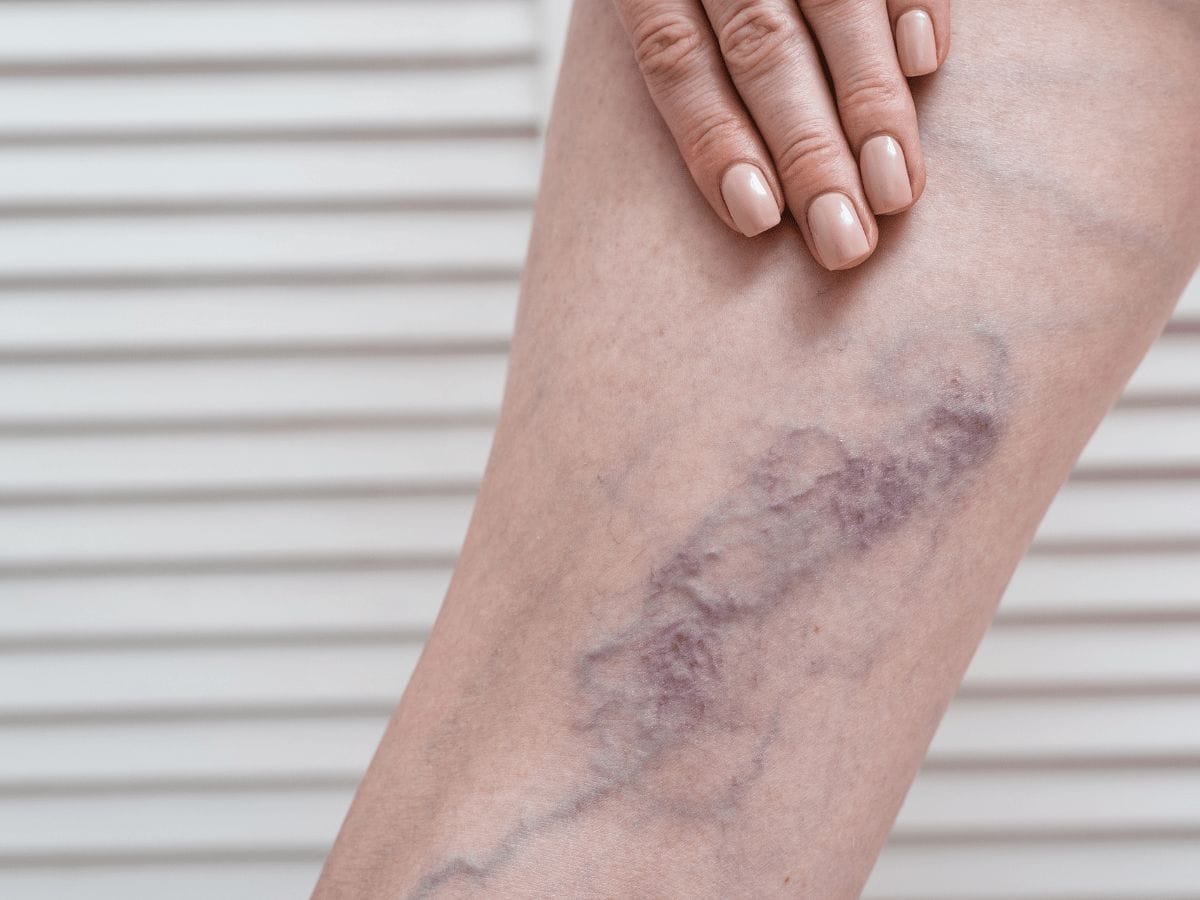
Deep Vein Thrombosis, or DVT, happens when a blood clot forms in our deep veins, usually in the legs. These clots can partially or completely block blood flow, leading to swelling, pain, and potentially severe complications. If you’ve ever felt a sudden tightness in your calf or noticed swelling in one leg, it might be more than just fatigue, it could be a serious health warning.
DVT becomes life-threatening when the clot breaks free, travels through the bloodstream, and lodges in the lungs. This is known as a pulmonary embolism (PE), a medical emergency with fatal consequences when left untreated. Together, DVT and PE form what’s known in the medical community as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
DVT doesn’t occur in a vacuum. It’s often the result of a combination of factors, and recognizing those risk factors is the first step in prevention. Here’s what increases your likelihood:
Prolonged sitting like during long flights, car rides, or hospital stays can drastically reduce blood flow in our legs. When blood flow slows down too much, clots can form.
Major surgeries, especially orthopedic procedures like knee or hip replacements, can damage veins and slow circulation, raising clot risk. Traumatic injury can have similar effects.
Inherited conditions like Factor V Leiden significantly increase clotting risk. If there’s a family history of blood clots, genetic screening could be worthwhile.
Hormonal changes affect blood coagulation. Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy are all known risk factors for women.
Cancer, heart failure, and inflammatory diseases increase the body’s tendency to clot. Cancer patients, in particular, are at higher risk due to both the disease and its treatments.
These lifestyle-related factors affect blood circulation and vessel health, increasing the risk of DVT.
Symptoms of DVT often go unnoticed in early stages or mimic less serious conditions making awareness crucial.
Keep in mind, some people don’t experience noticeable symptoms right away. That’s why risk assessment and regular monitoring are essential for those at higher risk.
Diagnosing DVT combines good clinical judgment with targeted diagnostics.
Doctors assess swelling, tenderness, changes in skin texture or color, and compare both legs if one seems different from the other.
This blood test measures a substance that’s released when a clot breaks down. Elevated levels can indicate clot presence but aren’t definitive on their own.
The primary imaging tool for DVT, it uses sound waves to visualize veins and detect clots. It’s non-invasive and highly accurate for identifying thrombosis in leg veins.
In rare cases, contrast dye imaging provides better visualization especially when clots are located in areas less accessible by ultrasound.
Treating DVT focuses on preventing clot growth, dislodgement, and recurrence.
The cornerstone of DVT treatment, anticoagulants (blood thinners such as heparin, warfarin, and newer agents like apixaban or rivaroxaban) stop clots from enlarging. They don’t dissolve existing clots but allow the body to break them down naturally.
In severe or life-threatening cases, clot-dissolving medications (e.g., tPA) may be used under strict supervision due to bleeding risk.
For patients who can’t take blood thinners, these filters are placed in a large vein (vena cava) to catch clots before they reach the lungs.
Rarely needed, this procedure physically removes the clot. It’s used only in extreme cases to prevent major complications.
Preventing DVT is often a matter of being proactive, especially if you fall into a high-risk group.
DVT doesn’t end when the clot forms. Major complications can have long-term health impacts.
When a clot breaks off and blocks blood flow in the lungs, it can cause sudden breathlessness, chest pain, and sometimes even cardiac arrest.
This chronic condition results from valve damage in the vein, causing pain, swelling, and skin changes that persist even after the clot resolves. It’s why long-term follow-up matters.
Once diagnosed and treated, managing DVT becomes a lifelong process for many. Adopting healthier habits has proven benefits.
We’ve seen patients completely change their future risk just by choosing better daily routines.
The world of DVT care isn’t static. Ongoing research continues to uncover faster diagnosis methods, smarter drugs with fewer side effects, and better tools to reduce recurrence.
If you’re experiencing unexplained leg swelling, pain, or have any risk factors for blood clots, don’t wait. Connect with South Florida Multispecialty Hospital’s vascular care team to get expert evaluation and personalized treatment. Your health and safety are too important to take chances.
DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. It’s dangerous because if the clot dislodges, it can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening.
Major risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, obesity, genetic clotting disorders, pregnancy, and smoking.
Diagnosis often includes a physical exam, a D-dimer blood test, and an ultrasound of the affected limb. In rare cases, venography or CT/MRI may be used.
Common symptoms include leg swelling, pain or cramping (usually in one leg), warmth, redness, and visible surface veins.
Treatment centers around anticoagulants like warfarin, rivaroxaban, or apixaban. In severe cases, thrombolytics, IVC filters, or surgical removal may be considered.
Stay hydrated, move frequently, use compression stockings, and in some cases, prophylactic anticoagulants may be recommended by your doctor.
Yes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, quitting smoking, and using compression stockings can help reduce future risk.
Untreated DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, which is a life-threatening emergency. Long-term, it can cause post-thrombotic syndrome, resulting in chronic pain and swelling.
Your well-being is our top priority. Reach out today to discover how our dedicated team can support your health journey.
Have questions or want to learn more? Use the form below to get started!
Connect with South Florida’s trusted multispecialty care team and take control of your health with compassion and convenience.
©2025 South Florida Multispecialty Medical Group. All Rights Reserved.